Indigestion Problem During Pregnancy.
Struggling with indigestion during pregnancy? Learn how hormonal changes affect digestion and discover expert-backed nutrition tips to ease discomfort and support your baby’s development.
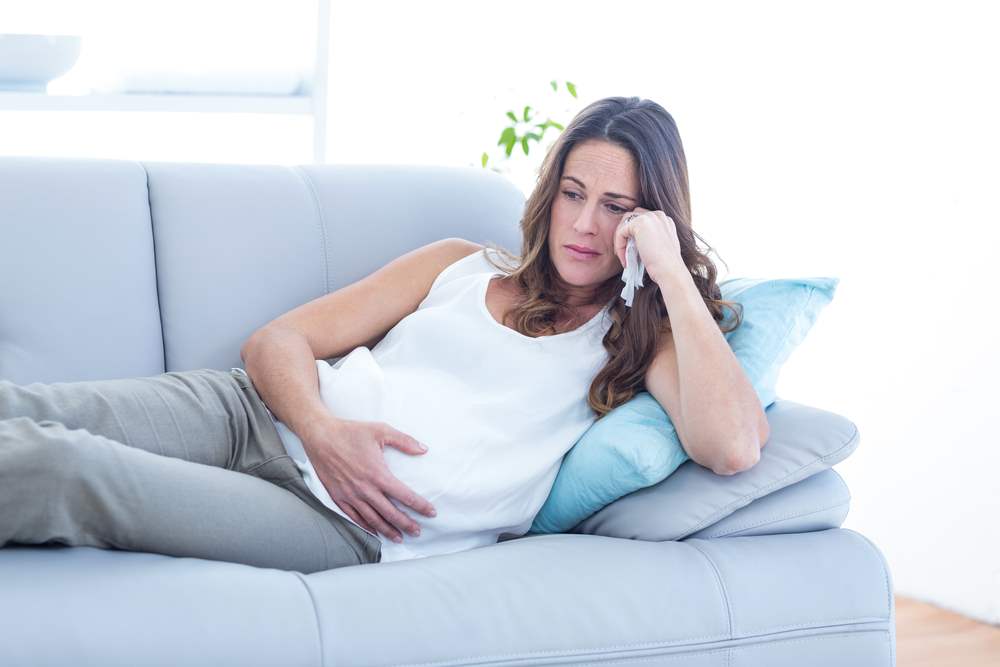

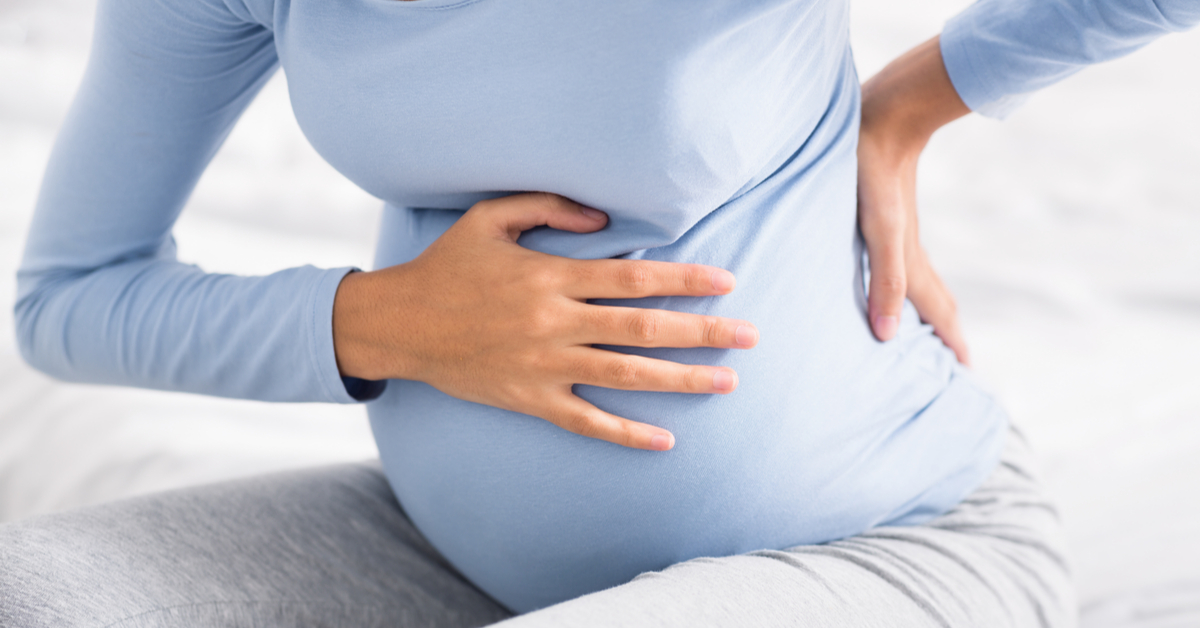
The exciting journey continues. Some of us have already heard the first heartbeat, while others are counting the days to hear it. As the effects of pregnancy become more pronounced, nausea may be accompanied by indigestion, which can significantly affect our quality of life during the day.
If you're experiencing something similar, don’t worry. Learning how to manage it will help you enjoy this beautiful period even more.
Indigestion during pregnancy is caused by the hormone progesterone, which slows down the movement of muscles. Its primary function is to prevent unnecessary uterine contractions, allowing the embryo to implant securely in the uterine wall. However, this hormone also relaxes stomach muscles, slowing down digestion. As a result, food is not digested as easily, leading to indigestion. In more advanced cases, it may even cause acid reflux or heartburn.
To reduce or eliminate these symptoms, you should first consult a doctor and a nutritionist. If a tailored nutrition plan isn’t enough to resolve your discomfort, your doctor may recommend safe medications to help you manage the issue.
Remember, you should never go hungry. If you don't want your baby to go without nourishment, you must also take care of your own needs. Eating small, frequent meals helps meet your daily nutritional needs. As nutritional requirements for vitamins and minerals increase during pregnancy, eating regularly becomes essential to cope with nausea and indigestion. This approach also supports your baby’s healthy development and maximizes nutrient absorption.
It’s important to stay away from sweets, as increased energy demands and irregular eating habits may cause sugar cravings. A personalized nutrition plan can gradually reduce your need for sweets. Also, cravings could be related to deficiencies, such as iron deficiency. Since sweets can become a habit, it’s best to avoid them—because whatever you eat, your baby eats too.
The nutritional content of your meals matters. Instead of focusing on calories, choose foods rich in nutrients and that provide long-lasting fullness. Your calorie intake shouldn't come mainly from carbohydrates, but from foods high in nutritional value and satiety.
Pay attention to seasonal eating. Choose fresh fruits and vegetables whenever possible, as this helps you avoid harmful processed foods. Fresh produce also helps preserve vitamin and mineral content. Stay away from frozen or long-stored foods, and always follow proper preparation and cooking methods. This will protect your digestive health and support your baby’s healthy growth.

 Admin
Admin